Abstract
Background: Platelet activation is essential for hemostasis. Central to platelet activation are the signals transmitted through surface receptors like GPVI, the protease activated receptors (PARs), and C-type lectin-like receptor 2 (CLEC-2). Clec-2 is a HemITAM-bearing receptor that binds podoplanin and signals through spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk). Syk activity is dependent on phosphorylation of several residues including Y348, Y352, and Y525/526 (Y342, Y346, and Y519/520 in mice). TULA-2 is a protein tyrosine phosphatase that is highly expressed in platelets, and targets phosphorylated Y352 of Syk. Therefore, we used TULA-2 knockout mouse platelets to determine whether or not TULA-2 regulates Syk phosphorylation and activity downstream of CLEC-2.
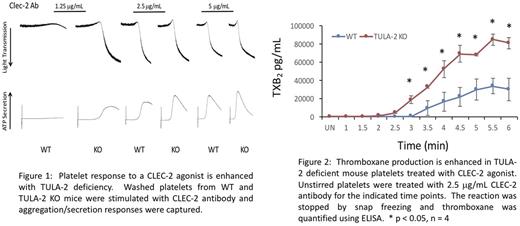
Results: Using washed platelets from WT and TULA-2 KO mice we determined that TULA-2 deficiency enhances the aggregation and secretion response following stimulation with an excitatory CLEC-2 antibody (Figure 1) or a CLEC-2 agonist rhodocytin. Consistently, Syk phosphorylation of Y346 is enhanced, as well as phosphorylation of the Syk substrate PLCγ2, in TULA-2 KO platelets treated with either CLEC-2 antibody or rhodocytin, compared to WT control platelets. Furthermore, the kinetics of Syk phosphorylation, as well as that of PLCγ2 and SLP-76 are enhanced in TULA-2 KO platelets treated with 2.5 μg/mL CLEC-2 antibody compared to WT platelets. Platelet activation results in secretion of granular contents as well as production of thromboxane, which serves to reinforce the primary excitatory signal and to activate other platelets. Similar to our results above, thromboxane production was enhanced, in both amount and kinetics, in TULA-2 KO platelets treated with 2.5 μg/mL CLEC-2 antibody (Figure 2).
Conclusions: TULA-2 acts as a negative regulator of CLEC-2 signaling by dephosphorylating Syk on Y352 and restraining subsequent Syk-mediated signaling.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal